Phone: 326 332 991
orthopeadics - procedures and examinations
MUDr. Daniel Horáček
ORTHOPAEDICS: TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
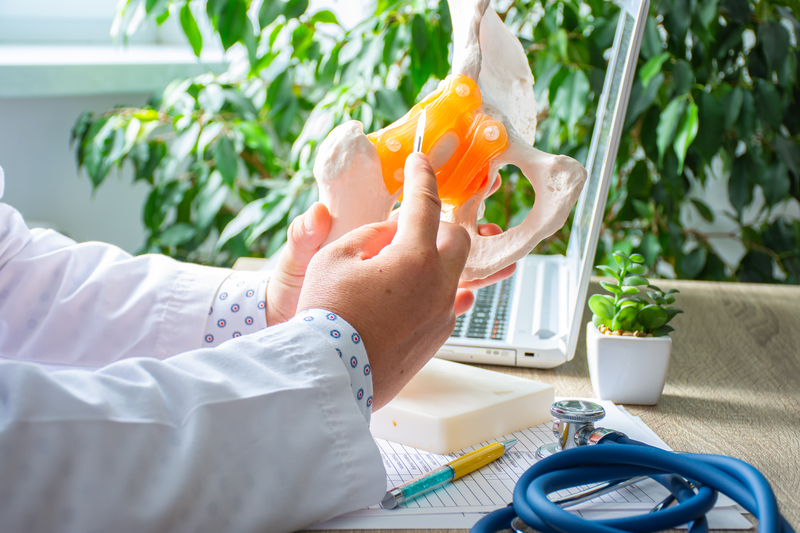
Anatomy of the hip joint
The hip joint is a spherical joint formed by the pelvic fossa (acetabulum) and the femoral head.
The bony base of the pelvic fossa is complemented by the cartilaginous labrum. Both bone surfaces are covered by hyaline cartilage in a healthy joint. The stability of the hip joint is due to the strong joint capsule and adjacent muscles, especially the m. iliopsoas, gluteal muscles and hamstrings. Blood vessels and nerves supplying the entire lower limb run around the hip joint.
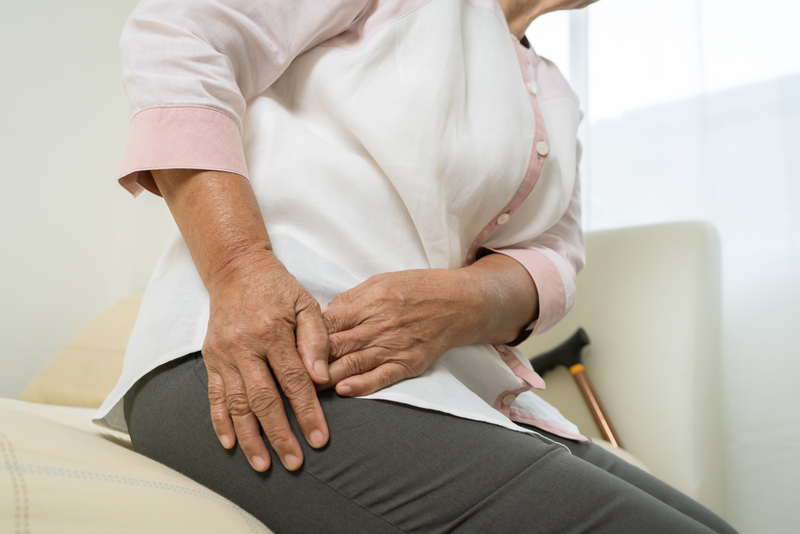
Hip arthrosis (coxarthrosis)
This is a degenerative, non-inflammatory disorder of the hip joint structures, initially manifested by pain on movement and joint stiffness. Later, resting and nocturnal pain also occurs. Starting pain in the morning and after prolonged periods of inactivity is also very common.
The cause may be:
- developmental dysplasia of the joint
- rheumatoid arthritis, Bechterew's disease
- post-traumatic disability, conditions following infectious complications
- conditions following aseptic necrosis (m. Perthes, corticosteroids)
Treatment of coxarthrosis
The treatment itself can be divided into conservative procedures, i.e. non-operative and operative procedures.
In the early stages of coxarthrosis, we use mainly pharmacological and rehabilitation procedures, with a strong emphasis on appropriate choice of sports activities.
Cycling and swimming are particularly suitable.
Weight control is important. In the advanced stage of arthritic hip disease it is often necessary to implant a total hip arthroplasty (THA).
The patient's difficulties are always decisive in deciding whether surgery is indicated.
Artificial joint - alloplasty - total hip arthroplasty (TEP)
Hip alloplasty is the replacement of a damaged joint with an implant.
Cemented endoprosthesis:
- A polyethylene socket fixed with bone cement.
- Bone cement-fixed stem
- most commonly a metal head with variable length
Hybrid endoprosthesis:
uncemented socket - usually titanium, with polyethylene insert
bone cement-fixed stem
metal alloy or ceramic head
Uncemented endoprosthesis:
- uncemented well - usually titanium, with polyethylene insert
- uncemented shank made of titanium alloy
- metal alloy or ceramic heads
Pre-operative preparation
Prior to total joint replacement, the patient undergoes a series of examinations and is coordinated by his or her treating physician throughout the preoperative preparation.
An integral part of the preoperative preparation is also the examination of inflammatory foci to exclude endogenous sources of infection in order to reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
Preoperative consultation with the anesthesiologist of our Clinic is also an advantage.
Basic scheme of preoperative examination:
1/ Exclusion of inflammatory foci (foci)
- Nose and throat swab for culture
- Urinalysis (in women, better catheterized urine)
- Dental examination
- Gynecological examination
2/ Preoperative internal examination including laboratory tests
Usually performed by the attending general practitioner in collaboration with an internist three weeks before surgery
The aim is to ensure the functional stability and reserves of the patient to cope with the surgical procedure and postoperative rehabilitation. Ensure proper safe adjustment of permanent medication if needed.
Before surgery, special attention is paid to adjusting the dosage of blood thinners, diabetes medications. Cannot perform surgery and take blood thinners at the same time.
Standard required examination:
ECG, RtgS+P,
Blood tests KO, INR APTT, Urea, creatinine, Na, K, Cl, bili, ALT AST, glucose, CRP
Urinalysis M+S
Other investigations are required in case of other chronic diseases.
Admission for surgery:
Day before surgery at 11.00 am. Patient may have breakfast and drink fluids on the day of admission. Patient will take his/her medicines with him/her on admission, if any
Surgery:
Before surgery - the surgeon will give the patient a detailed briefing on the surgical procedure, alternatives to surgery and post-operative treatment.
The time the patient spends in the operating room is individual. Upon arrival at our facility, an anesthesiologist will visit the patient and discuss with the patient the appropriate method of anesthesia and postoperative analgesia During surgery and immediately after surgery, we use procedures and systems that conserve blood loss.
Postoperative recovery:
After surgery, the patient is followed in the post-operative ward, where their condition is continuously monitored.
Further treatment then takes place in the monitored beds of our facility, where the patient is cared for by a team of experienced nurses, orthopaedic surgeons and physiotherapists.
The patient has his/her own personal physiotherapist throughout the stay. The average hospital stay after surgery is one week.
During this time, under the guidance of the physiotherapists, the patient learns basic self-sufficiency and how to walk on flat ground and up stairs.
After this time, the patient is usually able to be discharged for home treatment. Depending on the course of treatment and the provision of home care after discharge, the patient may remain in our Clinic for the follow-up treatment or we may arrange for transfer to an appropriate rehabilitation institute or spa.
For a detailed description of post-operative rehabilitation care during hospitalization, see. "Rehabilitation standards in orthopaedics".
Complications and risks:
Complications of total hip replacement are uncommon. Nevertheless, they can occur. They are mainly dislocation of the artificial hip replacement, infection of the endoprosthesis, weakening of the nerve function of the operated limb.
You will be informed in detail about all risks by your doctor during the outpatient examination. The doctor will also be happy to answer any further questions you may have.
Regimen recommendations for patients after total replacement can be found clearly on our website and will be repeatedly reminded during your stay with us.
See. Informed Consents.