Phone: 326 332 991
gastroenterologie - procedures and examinations
GASTROENTEROLOGY: STOMACH EXAMINATION
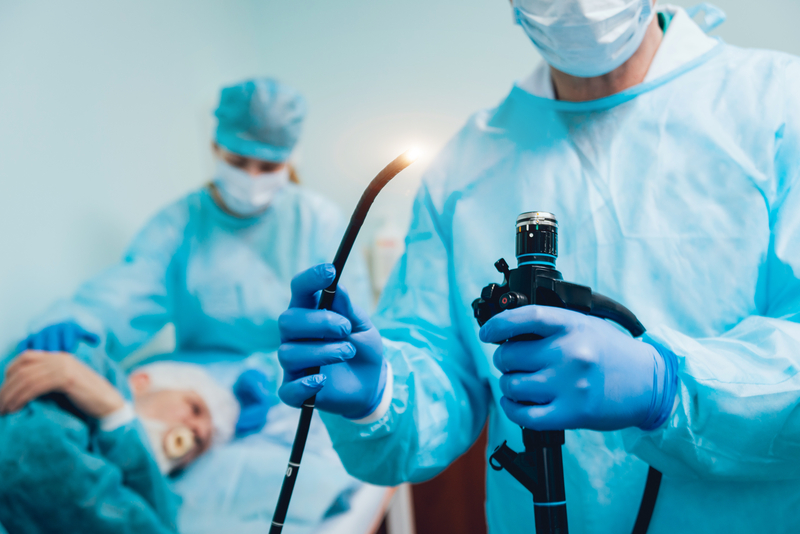
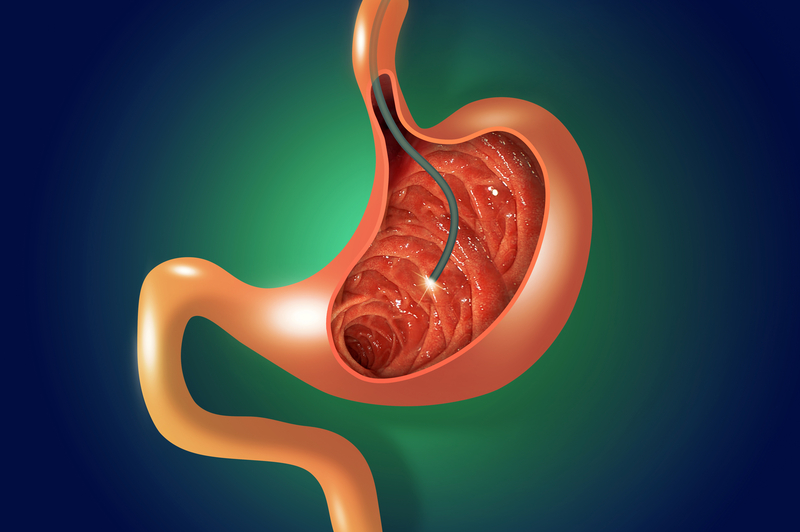
Gastroscopy is an examination with a flexible probe inserted through the mouth into the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum.
The examining physician watches an image transmitted by optical fibres and a video string on a TV screen.
In terms of quality, timeliness of diagnosis and the possibility of immediate gentle intervention (taking samples, stopping bleeding), it is an examination that is irreplaceable by any other method.
The purpose of the examination is to detect and evaluate a possible disease process in the area under examination or to monitor changes in the state of a process already known.
Before the examination
Before the examination, you should not eat, drink (possibly a small amount of clear liquid) or smoke for at least 8 hours. If the examination is performed in the morning, we recommend postponing the ingestion of morning medication until after the examination. Just before the examination, a numbing spray will be applied to the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
Examination
The examination takes place lying on your left side. The nurse will insert a mouthpiece into your mouth, which you will squeeze with your teeth or gums.
The doctor will then insert the device through the mouthpiece into your throat and then into your digestive tube. Initially, your cooperation is needed to swallow, but in the next stage the doctor inserts the device himself.
During the examination, the stomach has to be blown through the air, so you have to take into account the feeling of vomiting and gagging.
If the nature of your disease requires it, it is sometimes necessary to take biopsy samples, remove mucosal growths (polyps), in case of bleeding stop this. These procedures are more time-consuming, so the examination takes longer, but is painless.
After some procedures, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of subsequent short-term hospitalization. Otherwise, it is possible to leave the endoscopic unit immediately after the examination if the procedure is uncomplicated.
After the examination
The patient is advised on the treatment regimen, precautions after the procedure and scheduling of any further follow-up examinations. No precautions are needed after the proposed medical procedure, which was performed without complications, only eating and drinking no earlier than 30 minutes after the procedure.
After the intravenous administration of sedatives and painkillers (analgosedation), you must not drive a motor vehicle, ride public transport, drink alcohol, carry out tasks that require attention, make significant and legal decisions, or sign legal documents.
Instructions to the patient before the examination of the stomach (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
Characteristics
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is an examination of the upper part of the digestive tract.
This examination has been recommended to you on the basis of your complaints or as a preventive measure for early detection of possible disease changes.
The examination itself is performed with a flexible 12 mm diameter probe inserted by mouth into the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum. The examining physician watches an image transmitted by optical fibers and a video string on a TV screen.
In terms of quality, timeliness of diagnosis and the possibility of immediate gentle intervention (sampling, bleeding control), it is an examination that is not replaceable by any other method.
Duration of the examination: approx. 15 min.
Progress
Before the examination it is necessary not to eat for at least 8 hours, not to drink (possibly a small amount of clear liquid), not to smoke.
If the examination is performed in the morning, we recommend postponing the ingestion of morning medication until after the examination.
Inform the examining physician of any serious illnesses or allergies. A numbing spray will be applied to the nasopharyngeal mucosa before the device is inserted. The actual examination is started by inserting the device through the bite ring into the mouth and then into the digestive tube.
Vomiting and gagging should be expected. Initially, your cooperation is needed as you attempt to swallow later in the course, the doctor and nurse introduce the device themselves. During the examination, breathe calmly through your nose or mouth, do not swallow.
After an uncomplicated examination, you can leave the hospital immediately, you can eat and drink in 30 min.
Possible interventions and complications during the examination
Procedures that can be performed during the examination (taking biopsy samples, removing polyps, stopping bleeding, etc.) are painless, but sometimes require intravenous sedation followed by short-term hospitalization (1-2 hours).
On the day of sedative administration, patients are not allowed to drive motor vehicles and operate equipment requiring increased attention.
As with any invasive examination, gastroduodenoscopy may occasionally result in unexpected complications requiring hospital admission or surgical intervention. Injury to the oesophagus and stomach, up to perforation of the stomach wall, may occur. Mostly in the case of severe findings.
If unclear, consult the examining physician.